
If you’re thinking about investing in Cyprus’ economy by launching an IP business, it’s crucial to stay up-to-date on the latest legislation.
Cyprus offers a favourable investment climate for many businesses. New developments are always underway to further encourage foreign investors. One of the recent developments is known as the IP Box Regime.
Since July 2016, Cyprus has had regulations in place for intangible assets. The New IP Box Regime complies with OECD requirements and Profit Shifting (BEPS) recommendations. It’s also fully compatible with EU standards.
Benefits of Registering an IP or Research and Development Company in Cyprus
- Take advantage of Cyprus’ ideal investment climate, including extensive double tax treaties.
- Access EU markets & talented individuals
- Enjoy full legal protection from the EU
- Achieve an effective rate of 2.5% (or less)
Who & What Qualifies Under the New IP Regime?
Amendments to the Cyprus IP regime legislature introduced on 1st July 2016 (for intangible assets owned or developed after 1st July 2016) gave rise to a new IP Box Regime complying with OECD requirements and Profit Shifting (BEPS) Action 5 report. This in addition to the fact that the IP regime has been reviewed by the EU Code of conduct and has been assessed to be fully compatible with EU standards, as well as the fact that Cyprus has an extensive network of double tax treaties, allows Cyprus to remain an ideal location for registering an IP or Research and Development (R&D) Company.
1. Qualifying intangible assets
The revised law identifies a "qualifying intangible asset" as an asset which was acquired, developed, or exploited by a person to carry out/ enhance/ initiate a business being a result of R&D activities. Examples of these assets are patents (as these are provided by the Patents Law), copyright computer software programs and other IP assets which are per law non-obvious, useful and novel. For the above to apply and to be able to exploit the asset the person or group must not generate more than Euro 7.5 million or Euro 50 million respectively. Furthermore, the revised law has excluded business names, brands, trademarks, image rights and other intellectual property rights used within the scope of marketing products and services.
2. Qualifying Persons
Qualifying persons include:
- Cyprus Tax resident taxpayers
- Tax resident Permanent Establishments (PE’s) of non tax resident persons
- Foreign PE’s that are subject to tax in Cyprus
3. Qualifying profits
Qualifying Profits are calculated in accordance to the NEXUS FRACTION (used to determine the relevant deduction to the tax payer) and are derived by multiplying the overall income (OI) (of qualified asset) of the Company by the qualifying expenses (QE) (directly related to the qualifying asset) plus any uplift expenditure (UE), over the overall expenses (OE) of the business expenditure incurred specifically for the qualified intangible asset.
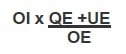
Overall income
Overall Income is calculated as the gross income less any direct expenditure of the asset. Under the revised law, 80% of the Overall income earned from the qualified intangible asset is treated as a deductible expense. The income earned from the qualified intangible assets may be but not limited to, royalties arising from the usage of a qualified intangible asset, income from selling a qualifying intangible asset and license revenue from operating the qualified intangible asset. Capital gains arising from the disposal of the qualified asset are not included in the overall income and are fully excempt from tax. The taxpayer has the right each year to elect not to claim the whole or part of the allowance.
In case of a resulting loss, only 20% of the loss can be carried forward to subsequent years.
Qualifying expenditure
Qualified expenditure refers to all costs (R&D costs) occurring throughout the year wholly and exclusively for developing/ improving/ creating a qualified intangible asset. These may include direct costs, wages and salaries, general expenses arising from installations used for R&D, various expenses associated with the supplies of R&D material, expenditure outsources to unrelated parties, etc. It should be noted that expenses related to acquisition of intangible assets or construction of immovable property, interest paid, and costs that took place for R&D and cannot be adequately substantiated are strictly prohibited as qualified expenditure and are excluded.
Uplift expenditure
The Uplift expenditure is added to the Qualifying Expenditure and as such is the lowest of:
- 30% of the Qualifying Expenditure, or
- The total cost of the acquisition and any R&D costs outsourced to related parties.
Overall Expenditure
The Overall expenditure is added to the Qualifying Expenditure and as such is the sum :
- The Qualifying Expenditure and
- The total cost of the acquisition and any R&D costs outsourced to related parties incurred in any tax year.
Learn More about Investing in Cyprus
Are you ready to invest in Cyprus? Learn more about why investing in Cyprus could be a good idea with our other article on the country’s investment climate.
Need some assistance ? Contact Papademetriou & Partners, INAA member in Cyprus !
